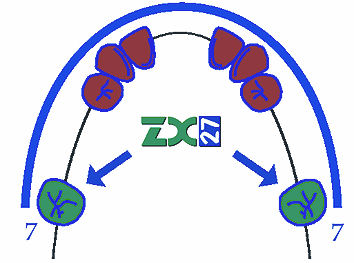
Basic principles required by glass abutment system ZX-27
- Common law: as many missing teeth are to be replaced distally, as many proper abutment teeth must be preparated mesially (with defects of 2a and 2b classes according to Kennedy).
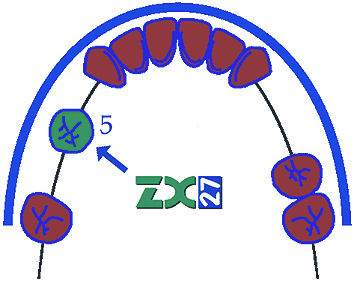
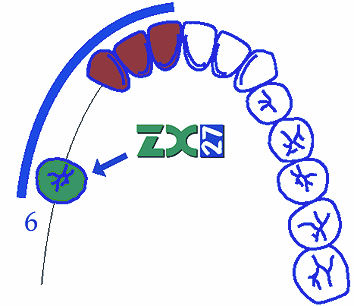
- The glass abutment is always the most distal part of the bridge in case of shortened dental arch (i.e. when replacing 5 and 6, it is ideal to grind 3 and 4, and 5 will make the intermediate tooth and 6 will be the glass abutment).
- From among the ground proper teeth, at least one abutment must be of 1st class. The more 1st class abutments ground, the better the result.
- The glass abutment must have an antagonist in order to renew articulation relations and teeth functionality.
Indications
- Target groups are patients between 30 and 60 years who have not yet had total prosthesis.
- Basic condition is to have a firm and pronounced alveolar crest in the area of prospective glass abutments ZX-27.
- obrúsený vlastný pilierový zub
- miesto skleneného piliera v mostíku
- rozsah fixného mostíka
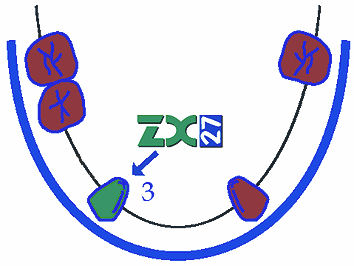
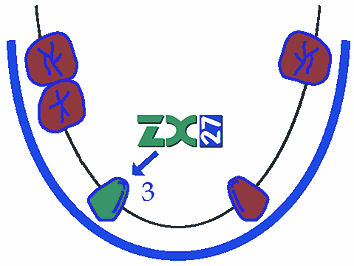
Kennedy 3 – with 3-4 missing teeth, ZX-27 may be used for supporting fixed dental bridges needed with decreased biological factor of abutment teeth,
Kennedy 2 – unilaterally shortened dental arch without gaps,
Kennedy 1 – bilaterally shortened dental arch without gaps,
Kennedy 2 – unilaterally shortened dental arch with gaps
Kennedy 1 – bilaterally shortened dental arch with gaps,
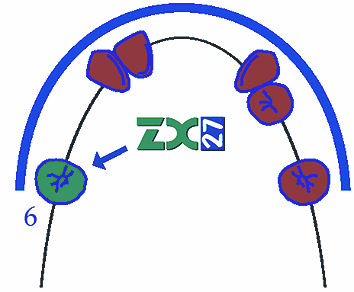
Kennedy 4 – solitary teeth; an ideal case is the so called favorable 3rd class case – inversely shortened dental arch.
Contraindications
- Unstable flabby crest (lateral movements of 5-8 mm)
- Insufficient alveolus height and width with elevated level of bone resorption.
- Very narrow alveolus in form of a narrow dental lamina made partially of submucous tissue.
- Insufficiently healed alveolus after extractions.
- Disease of oral cavity mucosa (leucoplakia, lichen ruber planus, etc) – recommended consultation with paradontologist.
- If the antagonist of the prospective glass abutment in the opposite jaw is in supraocclusion.